Summary 8.2
-Chloroplasts like chemical factories, with energy from the sun, coverting it to energy for plants
-Sunlight is a form of electromagnetic energy which travels in waves
-distance between two adjacent waves is called wavelength
-range of types of electromagnetic energy, from short gamma rays to long wavelengths of radio waves is electromagnetic spectrum

-visible light are wavelengths that your eyes see as different colors are only a small fraction of thespectrum
-Visible light consists of wavelengths from about 400 nanometers to about 700 nm
-Shorter wavelengths have more energy than longer wavelengths.
-pigments and substance's color is due to chemical compounds called pigments
- light shines on a material that contains pigments: they can be absorbed, transmitted, or reflected
-the chloroplast pigments do not absorb green light well asmost of the green light passes through the leaf (is transmitted) or bounces back (is reflected), looking green because the green light is not absorbed.
 |
-using paper chromotography, you could observe the different pigments in a green leaf
-he pigments dissolve in the solvents and are carried up the strip
-Different pigments travel at different rates, depending on how easily they dissolve and how strongly they are attracted to the paper
 |
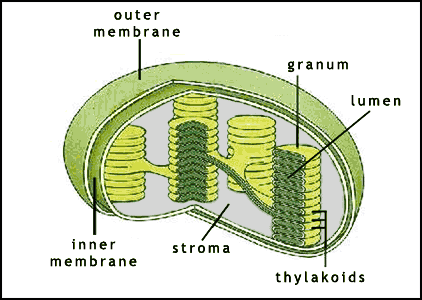
-within the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll and other molecules are arranged in clusters called photosystems which contains a few hundred pigment molecules
 |
-Each time a pigment molecule absorbs light energy, one of the pigment's electrons gains energy becoming very unstable
-Almost immediately,the excited electron falls back to the ground state and transfers the energy to a neighboring molecule, the energy "jumps" from molecule to molecule until it arrives at what is called the reaction center of the photosystem.
-Two photosystems are involved in the light reactions: first photosystem traps light energy and transfers the electrons to an electron transport chain, releases oxygen as a waste product, and also releases hydrogen ions. |
- releases energy which the chloroplast uses to make ATP.
-mechanism of ATP production is very similar to ATP production in cellular respiration as electron transport chain pumps hydrogen ions across a membrane
-main difference is that in respiration food provides the electrons for the electron transport chain, while in photosynthesis electrons from chlorophyll travel down the chain.
- second photosystem can be thought of as the "NADPH-producing photosystem."photosystem produces NADPH by transferring excited electrons and hydrogen ions to NADP+
 |
Concept Check 8.2
1. Explain why a leaf appears green.
A leaf appears green because the pigments located in the chlorphylls of the leaf do not absorb green light, therefore reflecting and bouncing off the light. When light shines on a material that contains pigments, three things can happen to the different wavelengths: they can be absorbed, transmitted, or reflected. The pigments in the leaf's chloroplasts absorb blue-violet and red-orange light very well. But the chloroplast pigments do not absorb green light well. Most of the green light passes through the leaf (is transmitted) or bounces back (is reflected) as leaves look green because the green light is not absorbed.
2. Describe what happens when a molecule of chlorophyll a absorbs light.
When a molecule of chlorophyll a which absorbs lightmainly blue-violet and red light and reflects mainly green light, it turns the substance into a green color. Chlorophyll a plays a major role in the light reactions of photosynthesis. Also, chlorphyll a is present in the reaction center which consists of a chlorophyll a molecule located next to another molecule called a primary electron acceptor. The primary electron acceptor is a molecule that traps the excited electron from the chlorophyll a molecule.
3. Besides oxygen, what two molecules are produced by the light reactions?
Besides oxygen, this process also releases hydrogen ions and NADPH molecules.
4. Where in the chloroplast do the light reactions take place?
The light reactions take place in both cases across a membrane—the inner mitochondrial membrane in respiration and the thylakoid membrane in photosynthesis.